This is the third and final post in a series of three on the ride sharing business. In the first, I valued Uber and looked at the evolution of its business over the last 18 months. In the second, I valued Lyft and looked at pricing across ride sharing companies. In this one, I look at the future of the ride sharing business from the perspective of an outsider with no expertise in this business.
In my last two posts, I first valued Uber, with its expansive narrative, and then looked at putting numbers on Lyft's less ambitious storyline. In my Uber post, I argued that the ride sharing market was proving to be bigger, broader and growing faster than I had estimated it would be in June 2014. In the Lyft post, I examined how VCs were pricing ride sharing companies. In this post, I want to complete the story by looking at the current state of the ride sharing market and for scenarios for the market over time, with consequences for investors, car riders and drivers.
The Ride Sharing Market: The State of the Game
In my posts on ride sharing, I noted that the ride sharing market has grown exponentially in the last two years, drawing in new users and redefining the car service business. That growth can be seen in multiple dimensions:
1. Anecdotal & Qualitative evidence: I am usually wary about using anecdotal data but I have been keeping tabs on Uber usage in my travels and I have been amazed at the company's global reach. This summer, I did seminars in So Paulo, Moscow and Mumbai, and in each venue, a significant proportion of the attendants had taken Uber to the event. In fact, my children talk about Ubering to destinations unknown, rather than taking a cab, just as xeroxing and googling became synonyms for copying and online searching.
2. Operating metrics at ride sharing companies: The operating metrics at the ride sharing companies individually, and in the aggregate, back up the proposition that this is a high growth business.
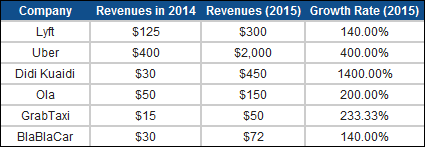
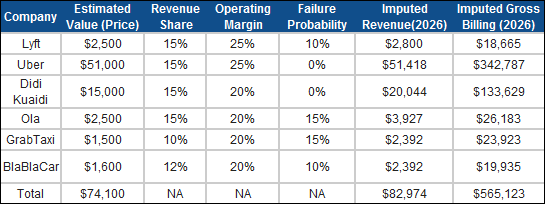
3. Investor expectations: The increases in the values attached to ride sharing companies indicate that investors are also scaling up expectations of future growth in this business. Using Uber's estimated value of $51 billion in its most recent VC funding to illustrate the process, I estimated imputed revenues of $51.4 billion in 2026, which, if you hold its revenue slice share at 15% (my assumption) yields an imputed gross billing of $342.8 billion in 2026. If I repeat this exercise with the other ride sharing companies, the collective revenues being forecast by investors may exceed attainable revenues, an example of what I termed the big market delusion.
The growth in ride sharing has been accompanied with more intense competition and rising costs, as can be seen in the large and growing operating losses reported by the companies in this business. The reasons for these losses are manifold, as I noted in my Uber post. Some of the costs come from intense competition for drivers and customers, with companies following the Field of Dreams model, that Amazon has used to such effect in the last decade. Some costs come from outside, higher insurance costs and employee expenses, as ride sharing companies go from being fringe players to larger businesses. Some costs flow from legal fights with regulators, licensing agencies and other rule-writers, whose desire to control the business clashes with the market-driven imperatives of ride sharing. The optimistic view is that these costs will become smaller as companies scale up, but will they? As revenues scale up, the number of drivers will increase proportionately, and unless the competition disappears, the costs of fighting for drivers and customers will continue. In brief, the existing ride sharing model looks like a long term money loser, unless something fundamental changes.
Future Shock
At the risk of playing market prognosticator in a market where I am a novice, I see four possible scenarios that can unfold in this market, all possible, but perhaps not equally probable.
- Winner-takes-all: The big prize in many technology businesses is that there is a tipping point, where the winner ends up capturing much of the market. That is the template that Microsoft used two decades ago with MS Office to capture the business software business and that Google used to scale the heights of online advertising. The payoff to such a strategy is that you not only control the dominant market share but that you get pricing power (and higher profits). It does seem to be the strategy that Uber is following in the ride sharing business, but there remain three road blocks that may get in the way. First, you have to remove your competitors from the playing field and while Uber had the cash buffer and capital raising upper hand last year, that advantage has narrowed as a result of partnerships and new capital flowing into other ride sharing companies. In a perverse way, Uber's best chance of succeeding at this strategy is if there is a hitch or stop in the flow of capital to tech companies, though that may work against its objective of going public in the near future. Second, you have to navigate your way through the anti trust and monopoly questions that will inevitably follow, not an easy or an inexpensive task, as Google and Microsoft have discovered over the last decade. Third, while technology remains a focal point for ride sharing companies, the car service or logistics business needs physical infrastructure, making it more difficult to preserve global networking benefits.
If these scenarios remind you a little little of the prisoner's dilemma, where two rational individuals are given a choice between cooperating and competing, there are parallels. Consider one possible version, where the ride sharing companies globally boil down to two competitors: Uber, as a global ride sharing behemoth, and the Not-Uber, an alliance of national ride ride sharing companies (Ola+Didi Kuaidi + GrabTaxi + Lyft..). The box below captures the possible outcomes of this game, which will get infinitely more complicated if there is an outsider player lurking on the fringes.
Based on my very limited knowledge of the companies in this space, I would give the highest odds to the ride sharing business becoming a loser's game, attach about equal probabilities to it becoming a winner-take-all or a game changer emerging, and see the least chance that the ride sharing companies will collude to maximize profits and value. There are others, who know more about this business than I do, who see this game evolving differently over time. Mark Shurtleff at Green Wheels Mobility Solutions, the ride sharing expert that I referenced in my last post thinks that I am being too pessimistic on some counts and perhaps too optimistic on others and feels that there are small start ups that are finding a better business model than the big players. There are some who believe that I am underestimating the pull of the familiar and that ride sharing companies, once established, will be difficult to displace.
The Dance of the Disrupted
In a post from a few months ago, I looked at the the dark side of disruption, i.e., the businesses being disrupted, both with the intent of identifying the businesses most at risk and to look at the stages, at least as I see them, of how the disrupted business deal with the chaos of seeing established business models being upended. Using that five stage process, it seems to me that the taxi cab business is now at an advanced stage:

So what does the future hold? Will there be no taxi cabs left on the streets of New York, London and Tokyo in a few years? I think that the taxi cab business will shrink, but not disappear, and that it will retain a portion of its business in those public spaces where regulators have the most say, airports, train stations and public arenas. If this is the future, it is also clear that there is more pain to come and it will take the form of continuing decline in taxi cab revenues and market capitalization at these companies. As for the private car service business, it will either adapt and share revenues with the ride sharing companies (which still needs cars and drivers) or focus on corporate relationships (offering discounted and on-demand services to companies that do not want their employees using multiple ride sharing services).
Coming soon to a business near you?
As I watch the traditional taxi cab business flailing and ride sharing companies grow at their expense, and am tempted to pass judgment on the inability of those in the business to adapt to the world that they live in, there are two general lessons that come to mind. From the disruptor's standpoint, I think that the success of Uber and its peer group in changing the car service business is a reminder that existing business models can be disrupted in short order by new technologies, but the collective losses reported by these companies are also a reminder that making money on disruption is much more difficult.
Looking at the same process from the perspective of the disrupted, it is a reminder that the pain inflicted on the car service business could very easily be coming to the business that you are in. If you are in the financial services business, the entertainment business or the health care business, all of which are deserving of disruption, I wonder whether you would react any more rationally than the London cabdrivers who went on strike to stop Uber, and ended up getting many of their customers to try Uber for the very first time. I operate in the education business, a large and extraordinarily inefficient business, and there is no group more resistant to change and more unprepared to adapt than tenured professors at research university. I cannot wait to see this group, convinced of its intellectual superiority and attached to unreal perks (minuscule teaching loads, research assistants and sabbaticals), go through the throes of disruption.
YouTube Version